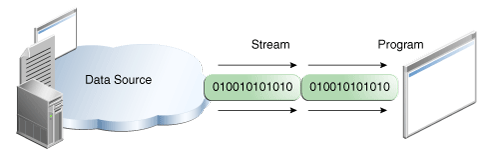
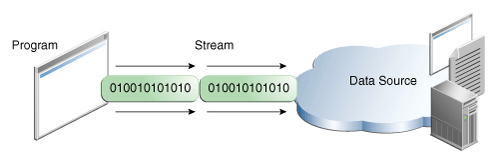
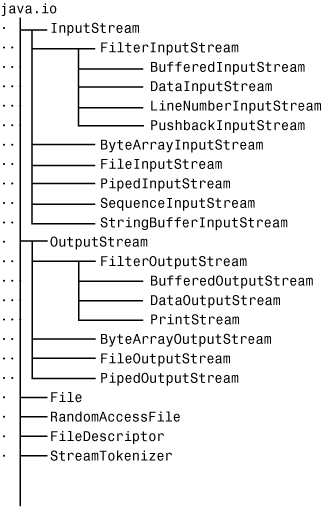
Java I/O streams
stream from/to everywhere
- screen
- file
- internet connection
- ...
transmit all kind of data
- byte, char, int, ...
- string, objects, ...


read() returns integer
(Unicode,
table)
read(): -1 at end
null: object not yet been instantiated
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
// normally just use import java.io.*;
public class CopyBytes {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// what happens if you would just use
// public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream out = null;
in = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
out = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
int c;
// --- start loop over all bytes in input file
while ((c = in.read()) != -1)
out.write(c);
// --- all reading has been done - close streams
if (in != null) in.close();
if (out != null) out.close();
} // end of CopyBytes.main()
} // end of CopyBytes
true catch exception
import java.io.*;
public class AppendBytes {
public static void main(String[] args) // no exception thrown
{
try {
FileInputStream inStream = new FileInputStream("input.txt");
FileOutputStream outStream = new FileOutputStream("output.txt",true); // append
// are equivalent: new FileOutputStream("output.txt",false);
// new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
// new FileOutputStream("output.txt",(1==2));
int c;
while ((c = inStream.read()) != -1)
outStream.write(c);
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of AppendBytes.main()
} // end of AppendBytes
This is an text input file
with a picture
,,,,,
* *
|* o o *|
* *
\ == /
..
PrintWriter: .print() .printf()
.flush()
import java.io.*;
public class FormattedOutput {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
PrintWriter myOutput = new PrintWriter("output.txt");
for (int i=0;i<8;i++)
myOutput.printf("%2d modulo 3 is %2d\n",i,i%3);
myOutput.flush(); // sent buffer to file
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of FormattedOutput.main()
} // end of FormattedOutput
BufferedReader: Reader .readLine()
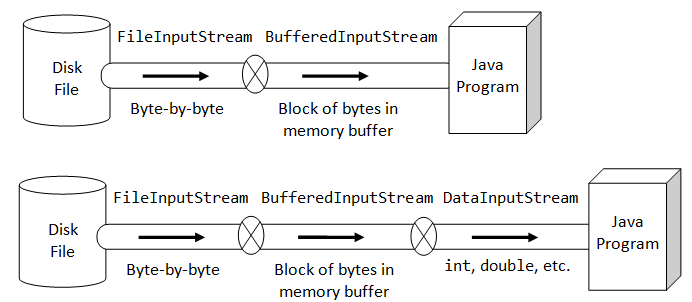
BufferedReader(Reader in) FileInputStream: byte Reader: 8 bits FileReader: char Reader: 16 bits
PrintWriter(File file)
writing via File object PrintWriter(OutputStream out)
writing via OutputStream PrintWriter(String fileName)
writing directly to file named fileName PrintWriter(Writer out)
writing via Writer PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush)
writing via Writer with (if true) autoflushString data line by line
import java.io.FileReader; // character reader
import java.io.FileWriter; // character writer
import java.io.BufferedReader; // buffering input
import java.io.PrintWriter; // formatting output
import java.io.IOException;
public class CopyLines {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
BufferedReader inputStream = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("input.txt"));
PrintWriter outputStream = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("output.txt")); // or ...
// PrintWriter outputStream = new PrintWriter("output.txt");
String s;
while ((s = inputStream.readLine()) != null)
outputStream.println(s);
outputStream.flush(); // send buffer to file
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of CopyLines.main()
} // end of CopyLines
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedOutput {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
PrintWriter myOutput = new PrintWriter( // for formatting
new BufferedWriter( // for buffering
new FileWriter("output.txt"))); // ouput stream
for (int i=0;i<8;i++)
myOutput.printf("%2d modulo 5 is %2d\n",i,i%5);
myOutput.flush(); // sent buffer to file
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of BufferedOutput.main()
} // end of BufferedOutput
import java.io.*;
public class PrintWriterDemo {
/** Use a single facility to send data to different streams,
* note the mandatory exception handling.
*/
static void printToStream(PrintWriter myOutput, String text)
throws IOException
{
myOutput.printf("this is the text: %s\n",text);
}
/** Always use buffered IO, it never hurts.
*/
public static void main(String args[])
{
try {
PrintWriter toFile =
new PrintWriter(new BufferedWriter(
new FileWriter("printWriterDemo.out")));
PrintWriter toConsole = new PrintWriter(System.out, true);
PrintWriterDemo.printToStream(toFile,"sending data to file");
PrintWriterDemo.printToStream(toConsole,"sending log data to console");
toFile.close();
toConsole.close();
} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
} // end of PrintWriterDemo.main()
} // end of class PrintWriterDemo
9 Mercury 0.0553 4880 5.43 0.000 58.81 d 0.387 87.97 d 0.2056 7.0 0.1 Venus 0.815 12104 5.20 0.000 243.69 d 0.723 224.70 d 0.0068 3.4 177.3 Earth 1.000 12742 5.52 0.0034 23.9345 h 1.000 365.26 d 0.0167 0.00 23.45 Mars 0.107 6780 3.93 0.0065 24.623 h 1.524 686.98 d 0.0934 1.85 25.19 Jupiter 317.83 139822 1.33 0.0649 9.925 h 5.203 11.86 y 0.04845 1.305 3.12 Saturn 95.162 116464 0.687 0.098 10.50 h 9.539 29.46 y 0.05565 2.489 26.73 Uranus 14.536 50724 1.32 0.023 17.24 h 19.182 84.01 y 0.0472 0.773 97.86 Neptune 17.147 49248 1.64 0.017 16.11 h 30.06 164.79 y 0.00858 1.773 29.56 Pluto 0.0021 2274 2.05 0.0 6.405 d 39.53 247.68 y 0.2482 17.15 122.46
Scanner(File file)
scanning via File object Scanner(InputStream inStream)
scanning via InputStream new Scanner(System.in) for console data input Boolean .hasNext() : has next entry, seperated by blanks String .next() : next entry as a String objectint .nextInt() : next entry as a int primitivedouble .nextDouble() : next entry as a double primitive (string1.equals(string2)) (string1==string2) is not secure
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DataInput {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try {
Scanner myScanner = new Scanner(
new FileInputStream("planetsData.list"));
// --- skippling initial comments
boolean readingComments = true;
while (readingComments)
readingComments = false;
// --- reading data
int nData = myScanner.nextInt();
String name;
double mass;
int diameter;
while (myScanner.hasNext())
{
name = myScanner.next();
mass = myScanner.nextDouble();
diameter = myScanner.nextInt();
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) myScanner.next(); // skipping rest of line
}
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of DataInput.main()
} // end of DataInput
Object class
public class MyClass implements Serializable{}
Array objects are serializable
per definition Object read
import java.io.*;
public class ObjectsIo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// ***
// *** generate objects and write objects to file
// ***
String[] stringArrayObject = {"This","is","an","array","of","strings"};
int[] intArrayObject = {4444,333,22,1};
try {
ObjectOutputStream myOutput = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("containsObject.txt"));
myOutput.writeObject(stringArrayObject);
myOutput.writeObject(intArrayObject);
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
// ***
// *** read objects from file
// ***
try {
ObjectInputStream myInput = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("containsObject.txt"));
Object obj = null;
while ((obj = myInput.readObject()) != null)
{
if (obj instanceof String[]) // String array ?
{
String[] ss = (String[])obj; // casting Object to String[]
for (int j=0;j<ss.length;j++)
System.out.printf("%s ",ss[j]);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
if (obj instanceof int[]) // int array ?
{
int[] ii = (int[])obj; // casting Object to int[]
for (int j=0;j<ii.length;j++)
System.out.printf("%d ",ii[j]);
System.out.printf("\n");
}
}
} catch (EOFException ex) { // EOF exception
System.out.println("End of file reached.");
} catch(IOException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println(e.toString());
}
} // end of ObjectsIo.main()
} // end of ObjectsIo
Write a program for object oriented input/output.
class Planet
storing all planet properties
System.getProperty() for various properties of
operating system .isDirectory() / .isFile()
for File objects
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
public class DirectoryHandling {
/** Give directory path as argument.
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
// ***
// *** open file handler / directory listing
// ***
String inputDirPath = null;
if (args.length==1)
inputDirPath = args[0]; // directory path
else
if (args.length==0)
inputDirPath = System.getProperty("user.dir"); // working directory
else
{
System.out.printf("number of arguments must be 0/1 and not %d\n",
args.length);
return; // exit main()
}
File inputDir = new File(inputDirPath); // open file or directory
String[] inputDirFiles = null;
if (inputDir.isDirectory()) // got a directory?
inputDirFiles = inputDir.list();
else
{
System.out.println("input not a directory: " + inputDirPath);
return; // exit main()
}
// ***
// *** (limited) output of directories/files found
// ***
String fileSeparator = System.getProperty("file.separator");
// is "/" on UNIX and "\" on Windows
//
System.out.println(" ");
System.out.println("files and directories found in: " + inputDirPath);
System.out.println(" ");
for (int i=0;i<Math.min(10,inputDirFiles.length);i++)
{
String fullPath = inputDirPath + fileSeparator + inputDirFiles[i];
File listFile = new File(fullPath) ; // open file or directory
if (listFile.isFile()) // got a file?
System.out.println("file: " + fullPath);
else
System.out.println(" dir: " + fullPath);
}
} // end of DirectoryHandling.main()
} // end of DirectoryHandling