address locations
- pointers point to the (start of the) memory address of an object
-
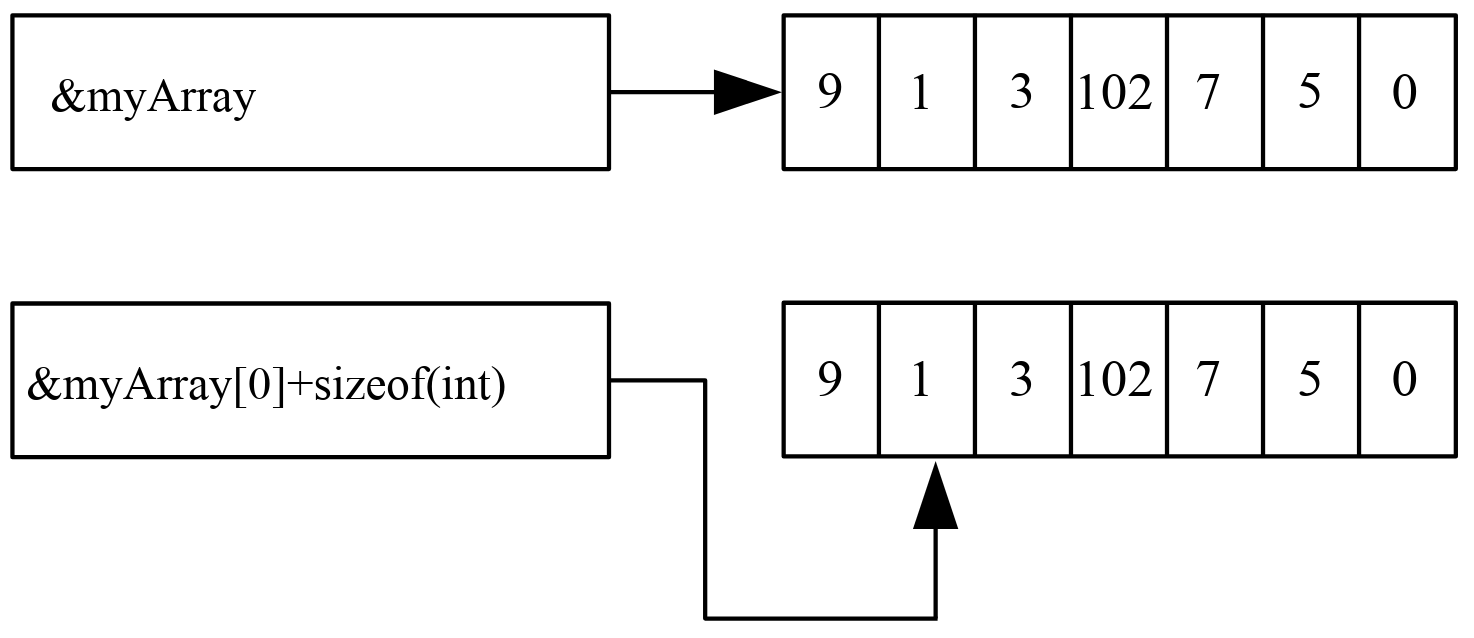
&variable: assessing the pointer of the variable (reference) -
int* intPointer: creates a pointer intPointer to an integer
*intPointer : assesses the value of the memory location
- pointers carry (in addition) the information about
the type (size) of adressed memory cell -
int** intPointPointer: a pointer pointing to an integer-pointer :: a two-dimensional int-array -
int intArray[]:
intArray is a pointer, pointing to the first element intArray[0] -
main(int argLength, char* argValues[])
argValues[] is an array of pointers - using pointer explicitly invites bugs to the party;
modern languages like JAVA do not allow it
Copy
Copy to clipboad
Downlaod
Download
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
int var1 = 20;
int var2[] = {1,2,3};
cout << endl;
cout << "address of var1: " << &var1 << endl;
cout << "address of var2: " << var2 << endl;
cout << "address of var2: " << &var2 << endl;
int* ip; // pointer variable
ip = &var1; // store address of var1 in pointer variable ip
cout << endl;
cout << "value of var1: " << var1 << endl;
cout << "value of ip: " << ip << endl;
cout << "value of *ip: " << *ip << endl;
ip = var2; // not &var2 (!), since arrays are already pointers
for (int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
cout << endl;
cout << "address of var2[" << i << "] = "
<< ip << " "
<< &(*ip) << " "
<< &var2[i] << endl;
cout << " value of var2[" << i << "] = "
<< *ip << " "
<< *(&(*ip)) << " "
<< *(&var2[i]) << endl;
ip++; // point to the next location (errors likely)
}
return 0;
}